The Gut-Brain Connection: How Your Gut Microbiome Impacts Mental Health

Do you ever wonder why your mood can sometimes be influenced by what you eat?
It turns out that there is a fascinating connection between your gut and your brain that plays a significant role in your mental health.
This connection, known as the gut-brain connection, is mediated by the gut microbiome – the community of bacteria and other microorganisms living in your digestive system.
In this article, we will explore the intricate relationship between your gut microbiome and your mental well-being, delving into how the gut-brain connection impacts your mood, cognition, and overall mental health.
When it comes to mental health, we often focus on factors such as genetics, environment, and stress.
However, recent research has shed light on the crucial role that your gut microbiome plays in shaping your mental state.
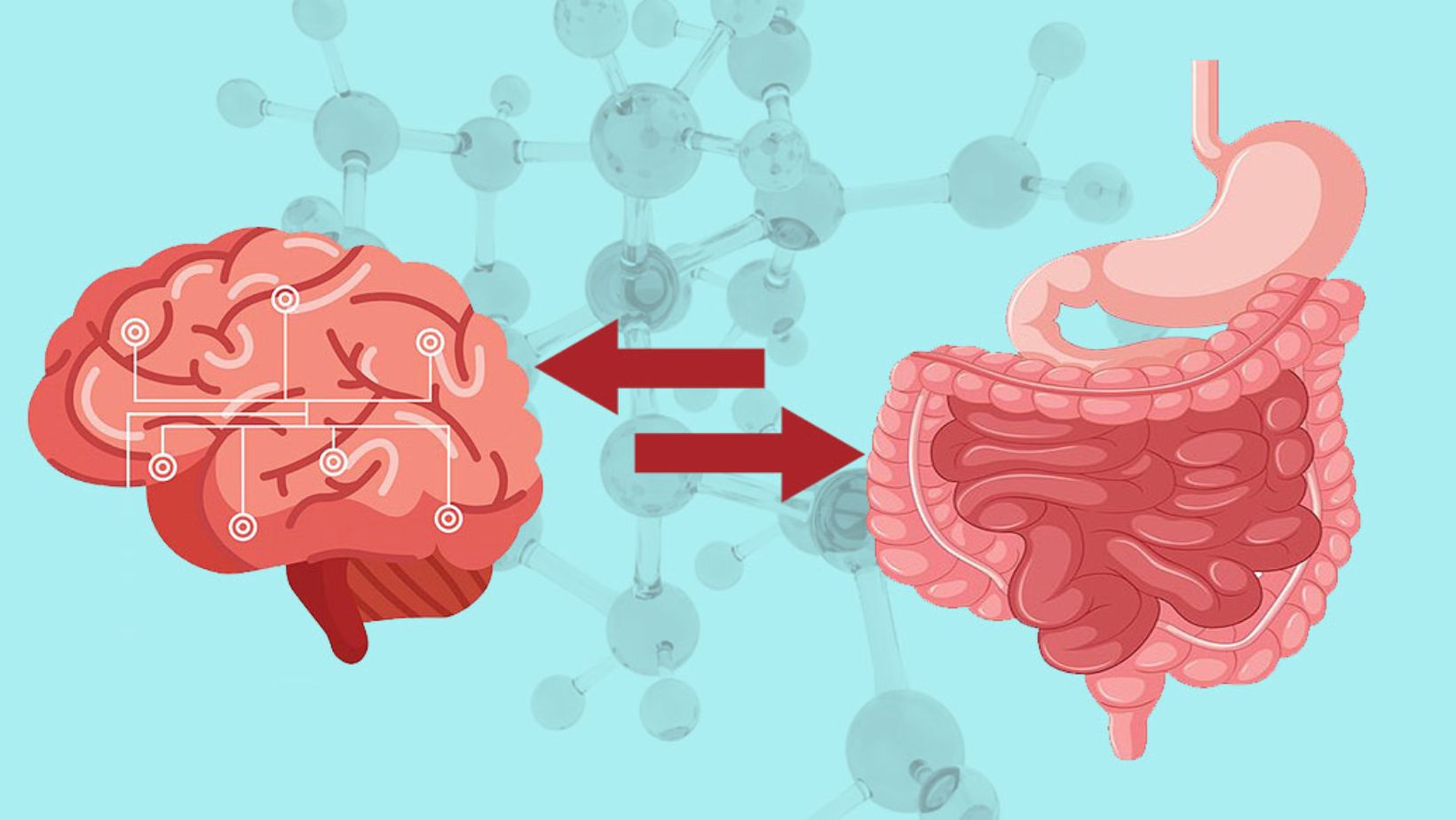
The gut-brain connection is a bidirectional communication system where signals from your gut can influence your brain and vice versa.
This means that what happens in your gut can have a profound impact on your mental health.
Understanding this connection is essential because it opens up exciting possibilities for potential therapies targeting the gut microbiome to improve mental well-being.
By exploring the intricate workings of the gut-brain axis, we can gain a deeper understanding of how our gut microbiome affects our emotions, cognition, and overall mental health.
So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of the gut-brain connection and discover how you can harness its power to optimize your mental well-being.
The Role of the Gut Microbiome in Mental Health
Your gut microbiome has the power to shape your mental well-being, so take care of it! The gut microbiome refers to the trillions of bacteria, viruses, and fungi that reside in your gastrointestinal tract. These microorganisms play a crucial role in various aspects of your health, including digestion, immune function, and even your mood.
Recent studies have revealed a strong connection between the gut microbiome and mental health. It turns out that the composition of the bacteria in your gut can influence the production of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which are essential for regulating mood and emotions. Therefore, maintaining a healthy balance of gut bacteria is vital for optimal mental well-being.
Furthermore, the gut microbiome also communicates with the brain through the gut-brain axis, a bidirectional pathway that involves neural, hormonal, and immune signals. This communication allows for a constant exchange of information between your gut and brain, influencing various aspects of your mental health, including stress response, anxiety levels, and even the development of mental disorders.
Imbalances in the gut microbiome, known as dysbiosis, have been linked to conditions such as depression, anxiety, and even neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Taking care of your gut microbiome involves adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet rich in fiber, fermented foods, and probiotics. Regular exercise, stress management, and getting enough sleep also contribute to a healthy gut microbiome and, consequently, better mental well-being.
The Gut-Brain Axis: How Communication Occurs
Discover the fascinating way in which your gut and your brain communicate with each other. The gut-brain axis is a complex network of communication that involves various pathways and mechanisms.
Here are four key ways in which this communication occurs:
- Neurotransmitters: Your gut produces and releases neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which play a crucial role in regulating mood and emotions. These neurotransmitters travel through the bloodstream and can directly affect the brain, influencing your overall mental well-being.
- Vagus nerve: The vagus nerve is a major pathway of communication between the gut and the brain. It sends signals back and forth, allowing for bidirectional communication. This nerve carries information about the state of your gut, including the presence of harmful bacteria or inflammation, which can impact brain function and mental health.
- Immune system: The gut is home to a large portion of your immune system, and immune cells in the gut can release molecules that can cross the blood-brain barrier and affect brain function. Inflammation in the gut can trigger an immune response that can also impact the brain, potentially leading to mental health issues.
- Microbiota metabolites: The gut microbiota, which consists of trillions of microorganisms, produces various metabolites that can influence brain function. For example, certain bacteria in the gut produce short-chain fatty acids, which i’ve been shown to have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects.
Understanding the gut-brain axis and how communication occurs between the gut and the brain is crucial in recognizing the impact of your gut microbiome on your mental health. By nurturing a healthy gut microbiota through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, you can positively influence your mental well-being.
Impact of the Gut Microbiome on Mood and Emotions
Nurturing a healthy balance of gut microbiota through lifestyle choices can significantly influence your emotional well-being. Research has shown that the composition of the gut microbiome is closely linked to mood and emotions.
The microbes in your gut produce neurotransmitters such as serotonin, which plays a key role in regulating mood. In fact, about 90% of serotonin is produced in the gut. When there is an imbalance in the gut microbiome, it can lead to a decrease in serotonin production, which may contribute to mood disorders such as depression and anxiety.
Furthermore, the gut microbiome also communicates with the brain through the vagus nerve, a major nerve that connects the gut and the brain. This communication pathway allows the microbes in your gut to send signals to the brain, influencing your emotions and behavior.
Studies have shown that altering the gut microbiome through probiotics or fecal microbiota transplantation can have a positive impact on mood and reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. Therefore, taking steps to maintain a healthy gut microbiome, such as consuming a diverse and balanced diet, exercising regularly, managing stress, and avoiding unnecessary antibiotics, can play a crucial role in promoting your emotional well-being.
Cognitive Effects of the Gut-Brain Connection
Imagine feeling more focused and mentally sharp just by making a few simple changes to your daily habits.
Well, the gut-brain connection has a significant impact on cognitive function. Research has shown that the gut microbiome, which consists of trillions of bacteria residing in your digestive system, plays a crucial role in influencing your brain health and cognitive abilities.
These bacteria produce various chemicals and neurotransmitters that can directly communicate with your brain, affecting your mood, memory, and overall cognitive function.
The gut-brain connection works through a complex network of nerves, hormones, and immune system molecules. When your gut microbiome is in a healthy state, it promotes the production of important neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are essential for regulating mood and cognition.
Additionally, certain bacteria in the gut produce short-chain fatty acids that can cross the blood-brain barrier and directly influence brain function.
By maintaining a diverse and balanced gut microbiome through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep, you can optimize your cognitive abilities and enhance your mental performance.
So, don’t underestimate the power of your gut when it comes to your brain health!
Potential Therapies Targeting the Gut Microbiome for Mental Well-being
Enhance your mental well-being by exploring potential therapies that target the gut microbiome. The gut microbiome has been increasingly recognized as a key player in mental health, and researchers are exploring various therapies that can harness its potential.
Here are three potential therapies that show promise in improving mental well-being:
- Probiotics: Probiotics are live bacteria and yeasts that are beneficial for our health, especially for our gut. These microorganisms can help restore the balance of good bacteria in the gut, which is essential for overall well-being. Research suggests that certain strains of probiotics can positively impact mental health by reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression. By introducing these beneficial bacteria into your gut, you may be able to support a healthier gut-brain axis and potentially improve your mental well-being.
- Prebiotics: Prebiotics are a type of dietary fiber that serves as food for the beneficial bacteria in your gut. Consuming prebiotics can help nourish and support the growth of these good bacteria, promoting a healthy gut microbiome. Studies have shown that a healthy gut microbiome is associated with improved mental health outcomes. By including prebiotic-rich foods in your diet, such as onions, garlic, bananas, and oats, you can potentially support a thriving gut microbiome and enhance your mental well-being.
- Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT): FMT involves transferring fecal matter from a healthy donor into the gut of an individual with a disrupted gut microbiome. This procedure aims to restore a healthy balance of bacteria in the gut and has been primarily used for treating conditions such as recurrent Clostridium difficile infection. However, emerging research suggests that FMT may also have the potential to improve mental health. While more studies are needed, early findings indicate that FMT could be a promising therapy for certain mental health disorders. It’s important to note that FMT is still an experimental treatment and should only be considered under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Exploring these potential therapies that target the gut microbiome can provide new avenues for improving mental well-being. By taking a proactive approach to support a healthy gut microbiome, you may be able to positively impact your mental health and overall quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, you now understand the incredible impact that your gut microbiome has on your mental health. The gut-brain connection plays a vital role in regulating mood, emotions, and cognitive function. The communication between the gut and the brain is constantly ongoing, and any disruption in this communication can lead to mental health issues.
It’s fascinating to learn how the gut microbiome can influence our emotions and cognitive abilities. By maintaining a healthy gut microbiome through a balanced diet and lifestyle, you can support your mental well-being. Additionally, researchers are exploring potential therapies that target the gut microbiome to improve mental health. This opens up new possibilities for treating conditions such as depression and anxiety in innovative ways.
In conclusion, taking care of your gut health is important not only for your physical well-being but also for your mental well-being. So, make sure to nourish your gut with a variety of nutrisystem for diabetics, exercise regularly, and manage stress levels.
By doing so, you can foster a healthy gut-brain connection and promote a positive mental state. Remember, a healthy gut means a healthy mind!